As a dog owner, it's fascinating to observe your furry friend's dental development. Puppies are born without teeth, but their first set of teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, start erupting when they're around 3-4 weeks old.
At 3-4 weeks, your puppy's first teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, start erupting, and by 6-8 weeks, they have a full set of 28 baby teeth. This first set of teeth is designed to fall out and make way for the permanent teeth.
These baby teeth are crucial for teething, which can be a challenging time for puppies. They help your puppy learn how to chew and bite, and their eruption is a significant milestone in their dental development.
By 6-12 months, most puppies have lost their baby teeth and have started to develop their permanent teeth.
Discover more: Dental Health Diets for Dogs
Canine Teeth Development
At around two weeks old, puppies start to grow their first puppy incisors. These are shortly followed by canine teeth and premolars.
By the time they're about 8 weeks of age, puppies have a complete set of baby teeth. Then you'll notice those teeth start to fall out.
Losing Baby Teeth
Losing baby teeth is a natural process for puppies, and it usually starts around 12 to 16 weeks of age.
Puppies typically lose their baby teeth in a specific order, starting with the incisors, followed by the canine teeth, and then the premolars.
Baby teeth have long roots, and trying to pull loose teeth out yourself can break a root, leading to possible infection.
It's normal to find a little tooth every now and then, and many baby teeth are swallowed, so don't be shocked if you discover your pup's baby teeth laying around the house.
Puppies will start to lose their first baby teeth around four months old, and between six and eight months of age, they should have lost all of their baby teeth.
The rate at which puppies lose their baby teeth can vary, but it's usually complete by the time they're eight months old.
If this caught your attention, see: Dogs Lose Puppy Teeth
Age-Related Milestones
At two months old, puppies start to get their adult teeth, and by the time they're seven to eight months old, they should have all 42 of their permanent teeth.
Suggestion: Shiba Inu 4 Months Old
Puppies grow their incisors, canine teeth, premolars, and molars at different stages. Incisors start coming in between two and four months, canine teeth between five and six months, premolars between four and six months, and molars between four and seven months.
Here's a rough guide to the timeline of adult teeth in puppies:
Knowing your puppy's age can help you give them the right care and lifestyle, and it's a good idea to check with your vet for a more accurate estimation of their age.
Care and Understanding
If your puppy is teething, it's essential to offer safe chew toys to help alleviate discomfort. These toys should be soft and flexible, bending easily in your hand.
Puppies in pain or reluctant to eat or play may need a veterinary appointment to rule out any underlying issues. Your veterinarian can provide specific recommendations for your puppy's needs.
For healthy puppies, teething shouldn't be a problem, as long as they're eating, drinking, and socializing normally.
On a similar theme: When Do Puppys Stop Teething
Caring for Your
Caring for your puppy during teething is crucial to ensure their comfort and safety.
Puppies learn about the world through their mouths, so it's natural for them to put everything in their mouth. They'll want to bite everything in sight, including furniture and your feet.
You can redirect their nipping by providing safe puppy teething toys. Freezing these toys can also provide a cooling treat.
Indestructible chew toys with tougher exteriors and textures can be a good option for super chewers. However, be careful not to choose toys that are as hard as a tooth, as they can crack a tooth.
If your puppy seems painful, reluctant to eat or play, or is showing any unusual behavior in their mouth, it's best to contact your veterinarian.
Soft and flexible toys that bend easily are the best for teething puppies. These toys can help relieve discomfort and satisfy their urge to chew.
Providing your puppy with appropriate chew toys, such as Kongs and rope toys, can help them feel more comfortable during the teething process.
Expand your knowledge: Can Dogs Chew Water Bottles
Understanding Your Dog's
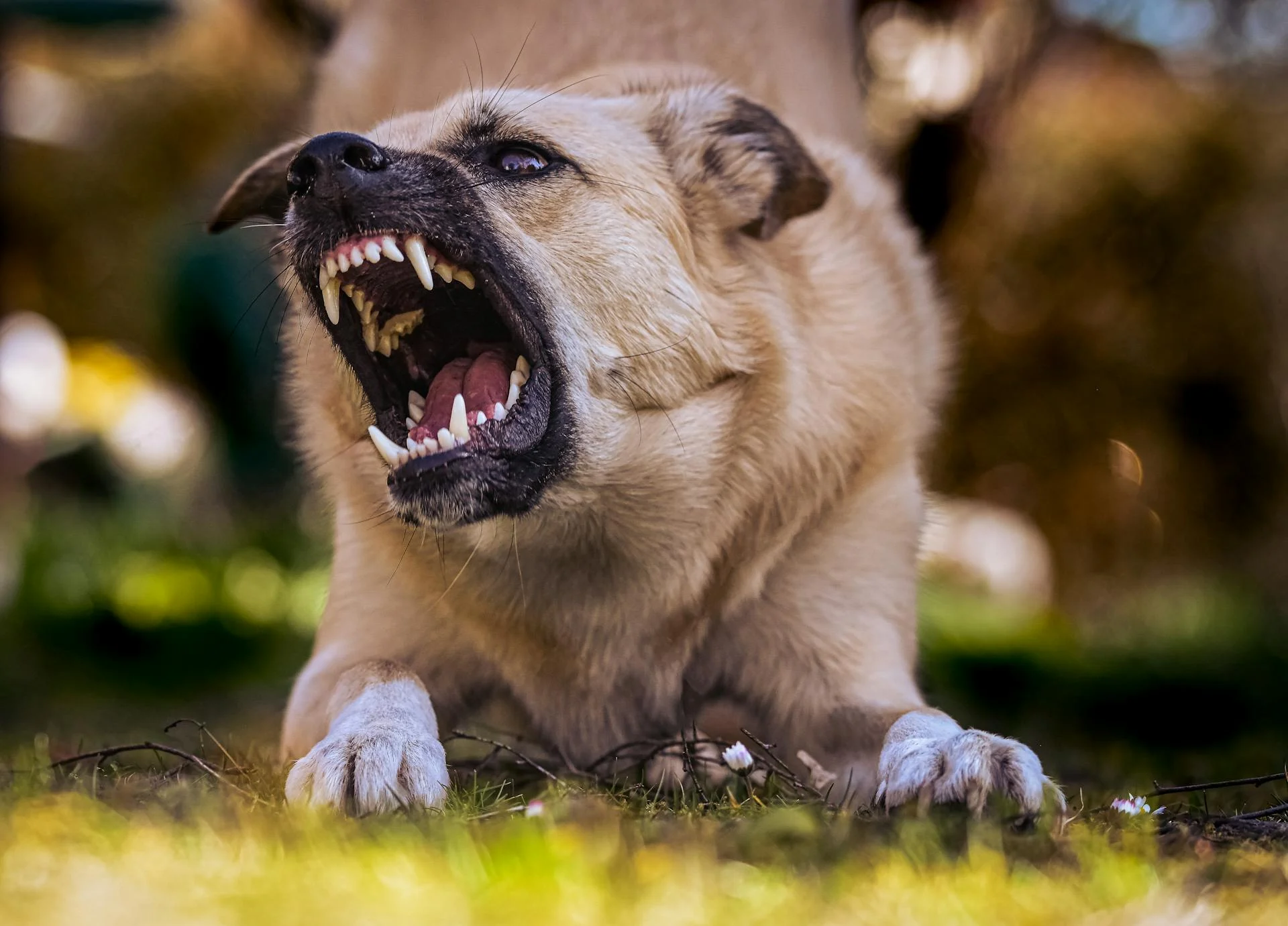
Dogs have four basic types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, found on both the upper and lower jaws.
These teeth are present on both the left and right sides of the jaw.
Puppies generally have around 28 teeth, which start growing in after three to four weeks.
Baby canines start coming in after three to four weeks, followed by baby incisors and premolars after four to six weeks.
By eight weeks, all baby teeth are grown in.
Tooth wear is a natural occurrence, but it can be accelerated by habits like aggressively chewing on hard objects.
Some chewing is great for a dog's dental health, and rawhides or "dental" chews can help dogs break down plaque and material on the teeth.
Here's a breakdown of the types of teeth your dog has:
Veterinary Care
Puppies start teething around three weeks of age.
Understanding the teething process can alleviate many concerns for new puppy parents. Puppies start teething around three weeks of age, and their baby teeth typically start to fall out around 12 to 16 weeks of age as their adult teeth come in.
Providing appropriate chew toys can help relieve any discomfort. Supervising your puppy is also crucial to prevent them from chewing on inappropriate objects.
If you have concerns about your puppy's teething or development, it's always best to consult with a veterinarian.
Expert Insights
Canine teeth are a crucial part of a dog's dental anatomy, and their development is closely tied to a dog's age.
Dogs typically start developing their canine teeth around 3-4 months old, and these teeth will continue to grow and erupt through the gums until they are fully formed at around 6-7 months old.
By 6 months old, most puppies have 28 deciduous teeth, including their canine teeth, which are designed for grasping and tearing food.
Canine teeth are also known as cuspids, and they are located in the upper and lower jaw, one on each side of the incisors.
In dogs, the upper canine teeth are slightly larger than the lower canine teeth, which is a characteristic that can be seen in many breeds.
A dog's canine teeth will continue to grow throughout their life, but the rate of growth slows down significantly after they reach adulthood.
The average lifespan of a dog's canine teeth is around 5-7 years, depending on factors such as diet, health, and genetics.
In some breeds, such as the German Shepherd, the canine teeth can be prone to wear and tear due to their active lifestyle and high energy level.
Regular dental care and check-ups can help prevent problems with a dog's canine teeth, such as tooth decay and gum disease.
A unique perspective: Could Shiba Inu Hit 1 Cent
Estimating and Understanding
Estimating your dog's age can be a bit tricky, but it's a great way to ensure you're giving them the best care possible. Evaluating a puppy's age by assessing its tooth growth is the most accurate time to determine their age, as teeth grow fast at the early puppy stage.
Counting the type and position of your puppy's teeth can give you a good estimate of their age. For example, if your puppy is two months old, you can expect to see adult teeth starting to erupt. By the time they're four months old, incisors should be present, canine teeth at five or six months, premolars at four or six months, and molars at four to seven months.
As your puppy grows into an adult dog, evaluating the condition of their teeth can help estimate their age. In the first two years of adult life, teeth are generally white with very little wear, but by the end of the second year, the white will have dulled and tartar will begin building up, causing yellowing on the back teeth.
For more insights, see: Two Pit Bulls
It's worth noting that food, habits, and dental care can all play a role in hastening or slowing teeth wear in dogs. If you're unsure about your dog's age, consulting your vet is always a good idea.
Here's a rough estimate of when you can expect your puppy to have their permanent teeth:
As your dog ages, you can use the amount of wear and tartar accumulation on their teeth to determine their age. Typically, dog teeth become less pointed after about 5-6 years of age, depending on their routine and dental care.
Sources
- https://www.pumpkin.care/blog/when-do-puppy-teeth-fall-out/
- https://bettervet.com/resources/pet-health-care/puppy-teething
- https://veterinarydental.com/puppies-lose-teeth-boxborough-ma/
- https://embarkvet.com/resources/puppy-age-using-their-teeth/
- https://www.wikihow.com/Determine-Your-Dog%27s-Age-By-Its-Teeth
Featured Images: pexels.com


