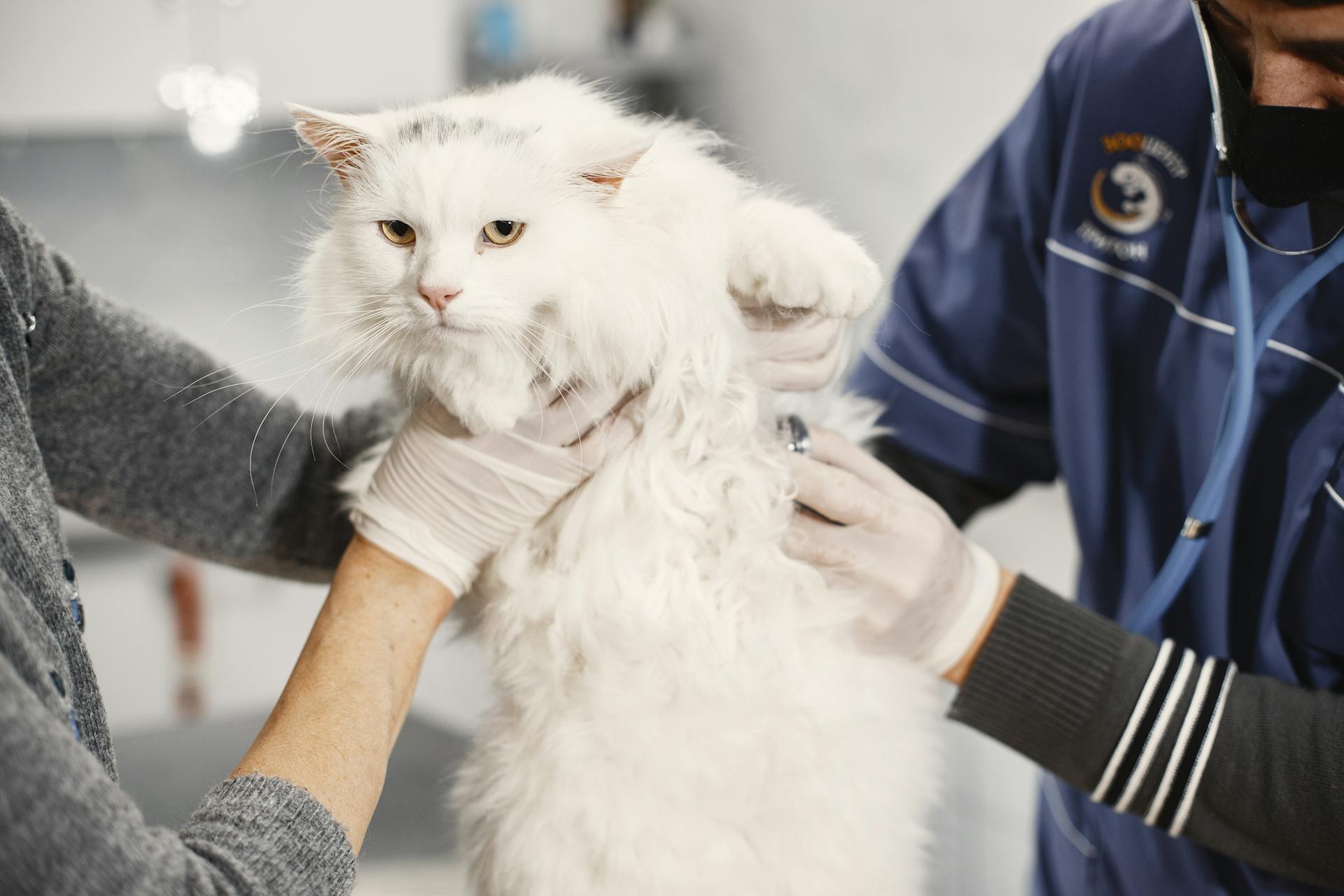
Reverse sneezing in cats can be unsettling to witness, but it's a relatively common condition that can be triggered by various factors.
The sound of a cat's reverse sneeze is often described as a loud, high-pitched honking or snorting noise.
Cats may exhibit a range of behaviors during a reverse sneezing episode, from simply standing still to violently thrashing their head and neck.
In most cases, reverse sneezing in cats is not a cause for concern and can be easily treated at home.
What Causes Cat Reverse Sneezing?
Reverse sneezing in cats is a common phenomenon, but what causes it? The precise cause remains elusive, but several potential triggers can instigate these episodes.
Environmental irritants and allergens, such as dust, pollen, strong odors, smoke, or even fleas and ticks, can trigger irritation in a cat's eyes and sinuses, leading to inflammation of the nasal passages and provoking the reverse sneezing reflex.
Some cats may display reverse sneezing episodes during periods of excitement or anxiety, as a response to elevated emotional states or physical exertion.
Nasal mucus or post-nasal drip, potentially resulting from allergies, upper respiratory infections, dental diseases, or other underlying conditions, can stimulate the reverse sneezing reflex.
A common presentation in cats is grass that has become trapped behind the soft palate, which can often be dealt with by flushing the sinuses but may require removal under a general anesthetic.
If infection is the cause, you can expect to see additional signs, such as nasal discharge, watery or sticky eyes, inappetence, and lethargy.
Other potential causes include nasal mites, nasal tumors, a foreign body in the nose, or issues with the soft palate.
Here are some common causes of reverse sneezing in cats:
- Environmental irritants and allergens
- Nasal mucus or post-nasal drip
- Excitement or stress
- Nasal mites, tumors, or foreign bodies
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of reverse sneezing in cats are often noticeable, with abrupt and frequent inhalations being a common sign. These inhalations can be quite loud, resembling a snorting or gasping sound.
A cat experiencing a reverse sneezing episode might stretch out their head and neck, which helps open the airways and enhance airflow. This posture is often accompanied by snorting or snuffling sounds.
Reverse sneezing episodes typically don't last long, usually concluding in less than a minute. Your cat should return to their regular breathing pattern once the episode subsides.
A veterinarian may conduct evaluations to exclude other underlying respiratory conditions and validate the diagnosis of reverse sneezing. This can include physical examination, chest x-rays, and rhinoscopy.
If you're unsure whether your cat is experiencing a reverse sneeze or if the frequency of sneezing becomes chronic, it's best to consult a veterinarian for a proper evaluation and guidance.
Symptoms of Cats
Cats experiencing a reverse sneezing episode will often display abrupt and frequent inhalations through the nose, which can be quite loud and resemble a snorting or gasping sound.
These inhalations can be a telltale sign of a reverse sneezing episode, and they're usually accompanied by other symptoms like extension of the head and neck, which helps open the airways and enhance airflow.
A cat in the midst of a reverse sneezing episode might also make audible snorting sounds, and they may maintain a rigid body posture, standing still or bending slightly over.
Typically, reverse sneezing episodes don't last long, concluding in less than a minute, and your cat should return to their regular breathing pattern once the episode subsides.
Here are some common symptoms to look out for during a reverse sneezing episode:
- Abrupt, frequent inhalations
- Extension of the head and neck
- Audible snorting sounds
- Rigid body posture
- Brief duration
Testing and Diagnosis
Occasional reverse sneezing is normal, but if it persists or increases in severity, diagnostics may be indicated to test for feline asthma or other respiratory/nasal conditions.
If you've never seen a reverse sneeze before, it can be tricky to distinguish it from other symptoms like coughing or choking.
Veterinarians may conduct physical examinations, chest x-rays, and rhinoscopy to diagnose reverse sneezing and rule out other underlying conditions.
Keep in mind that there's no specific diagnostic test for reverse sneezing, so veterinarians rely on observing clinical signs and characteristic episodes.
A record of the sneezing episodes, noting the duration, frequency, and any potential triggers or accompanying symptoms, will be invaluable to your veterinarian in diagnosing and advising on any necessary treatments.
Readers also liked: Canine Brucellosis Test
Treatment and Prevention
Most episodes of reverse sneezing in cats last less than a minute and settle on their own once the stimulus has subsided.
If the sneezing persists, you can try using a gentle coupage method to help open up the airways and force air up through the nasopharynx.
Making an appointment with your vet is recommended if the problem persists or if your cat is experiencing regular episodes of reverse sneezing.
Annual checkups with your vet can help detect minor changes and subtle signs of health issues before they become major problems.
Treatment for
In most cases, no treatment is needed for reverse sneezing in cats and dogs. The sneezing episode will usually settle once the stimulus has subsided.
Most episodes of reverse sneezing last less than a minute. They can be over as quickly as they started.
If an episode lasts longer than a minute, you can try using a gentle coupage method to help open up the airways. This involves placing one palm flat against one side of the chest and gently patting the other side with the other hand.

Frequent or persistent episodes of reverse sneezing should be explored with your family veterinarian. They may refer you to a board-certified veterinary internal medicine specialist if advanced diagnostics are needed.
Annual checkups with your vet are essential for detecting minor changes and subtle signs of illness in your pet. This can help prevent issues with the heart or lungs, changes or lumps in the abdomen, inflammation of the ears or throat, and dental disease.
Cat Prevention
To help prevent or minimize episodes of reverse sneezing in cats, pet owners can consider the following.
Using antihistamines under veterinary guidance can help manage reverse sneezing associated with allergies. However, not all cats respond well to antihistamines.
Be mindful of grooming products or sprays that irritate your cat's respiratory system. Choose gentle and hypoallergenic grooming products.
While it may not be possible to prevent reverse sneezing in all cats completely, these preventive measures can help minimize the frequency and severity of episodes.
Take a look at this: How to Prevent Diabetes in Dogs
Surgery or Intervention

Surgical intervention is usually reserved for severe and persistent cases of reverse sneezing in cats.
In rare cases, structural abnormalities or anatomical obstructions in the airway can contribute to reverse sneezing, making surgery necessary to alleviate symptoms.
Surgical removal may be necessary to alleviate symptoms if there is evidence of nasal polyps or other obstructive masses.
Veterinarians will tailor the treatment plan to each cat, considering their overall health and specific needs.
Regular follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor the cat's progress and adjust the treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you tell if a cat has a reverse sneeze or asthma?
To determine if your cat is experiencing a reverse sneeze or asthma, look for a stiff neck, snorting sounds, and difficulty breathing, which can be a sign of a reverse sneeze. However, if your cat's symptoms persist or worsen, consult a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Sources
- https://beyondpets.com/pet-health-plus/reverse-sneeze-in-cats/
- https://vetster.com/en/symptoms/cat/reverse-sneezing-in-cats
- https://cheyennepets.com/cat-reverse-sneezing-what-is-it-and-how-to-help-your-cat/
- https://www.catster.com/ask-the-vet/reverse-sneezing-in-cats-vet-answer/
- https://criticalcaredvm.com/reverse-sneezing-dogs-cats/
Featured Images: pexels.com