Sebaceous adenitis is a skin condition that affects companion animals, particularly dogs and cats. It's a rare and chronic condition that can cause significant discomfort and distress for affected animals.
The condition is characterized by the inflammation and destruction of sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing oils that help to keep the skin and coat healthy.
Sebaceous adenitis can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including immune system dysfunction and exposure to certain allergens or irritants.
What Is Sebaceous Adenitis?
Sebaceous adenitis is a rare skin disorder that affects the sebaceous glands, leading to inflammation and destruction.
It primarily affects the sebaceous glands, resulting in their degeneration.
Sebaceous adenitis can occur in dogs and humans, with different age and demographic groups affected.
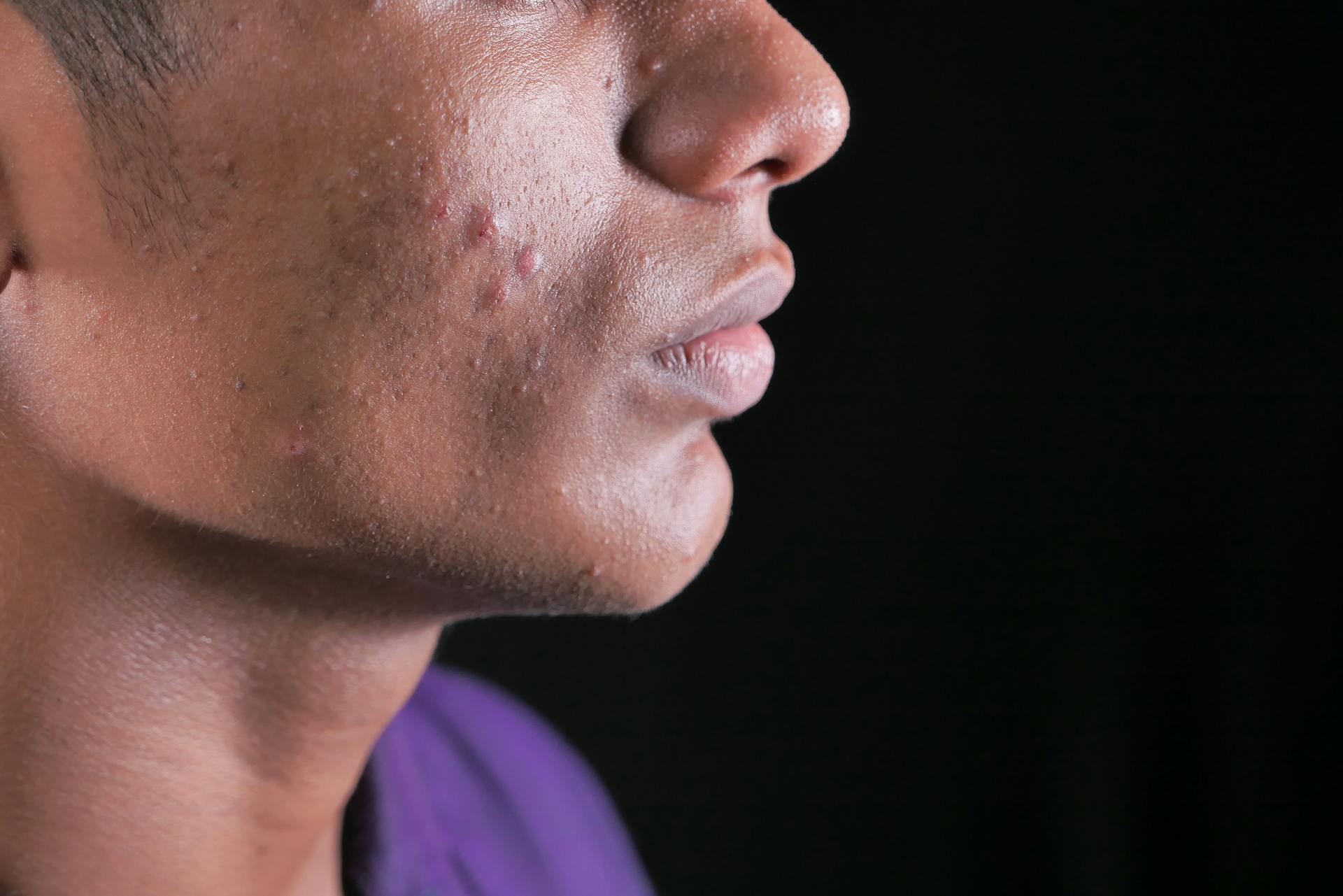
In humans, it often affects young men, particularly on the face and torso.
In dogs, the condition is more common in certain breeds, but the exact breeds are not specified.
The symptoms of sebaceous adenitis may vary, but often include hair loss, erythema, and the presence of follicular casts.
More severe cases can lead to secondary infections, which can complicate the condition.
The definitive diagnosis of sebaceous adenitis is based on a combination of history, clinical presentation, and histopathology.
Suggestion: Is Kennel Cough Contagious to Humans
Causes and Risk Factors
Sebaceous adenitis is a complex condition with multiple potential causes and risk factors. The exact cause is unknown, but it's believed to have a multifactorial origin.
Genetic predisposition is strongly suspected to play a significant role in the development of this condition, with some breeds like the Akita and Poodle being more prone to it. In fact, it's assumed to follow an autosomal recessive mode in these breeds.
Immune system dysfunction is also believed to be a major contributor to the etiology, with glandular destruction linked to a cell-mediated immunologic response targeting the glands. This is supported by the presence of dendritic antigen-presenting cells and T-cells in affected individuals.
Environmental factors like stressful events, heat, and sunlight exposure can also initiate or exacerbate the condition. For example, one case report showed a close association with Demodex mites adjacent to the adenitis, suggesting that environmental factors may play a role.
Readers also liked: Environmental Allergies Dogs
What Causes?
Sebaceous adenitis is a complex condition, and the exact cause is still unknown.
Research suggests that the inflammatory disease process that affects the sebaceous glands may have different underlying causes in different breeds of dogs.
In Standard Poodles, sebaceous adenitis is likely an autosomal recessive inherited disease, meaning that a dog must inherit two copies of the mutated gene, one from each parent, to develop the condition.
The cause of neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis is also unknown, although light exposure may exacerbate the condition in some cases.
In some breeds, such as the Akita and Poodle, sebaceous adenitis is believed to follow an autosomal recessive mode, and ongoing studies are seeking to identify specific genetic markers and mutations that may contribute to susceptibility.
Genetic predisposition is strongly suspected to play a significant role in the development of sebaceous adenitis, and immune system dysfunction is also believed to be a major contributor to the condition.
A cell-mediated immunologic response targeting the sebaceous glands is linked to glandular destruction, and immunohistologic analysis has revealed the presence of dendritic antigen-presenting cells and T-cells concentrated in the middle part of the follicle.
Exposure to sunlight can further worsen the disease, and other environmental factors, such as stressful events and heat, may initiate or exacerbate the condition.
Broaden your view: Canine Vector-borne Disease
Who Gets?

If you're wondering who gets neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis, the answer is a bit surprising. This condition is extremely rare, affecting less than 15 individuals, with most of them being young men.
Only a few cases have been described in women, so it's not a condition that's commonly seen in the general population.
Clinical Presentation
Sebaceous adenitis can affect dogs of various ages, but it typically develops in young to middle-aged adult dogs. Males are more likely to be affected than females.
The condition often starts with follicular casts, scaling, and hypotrichosis, particularly on the head. These symptoms are seen in 92% of cases, followed by the development of pyoderma in 42% of dogs.
Follicular casts are keratinized material that envelops the hair like a cast on a limb, and they're considered the hallmark of the condition in long-haired breeds. In some dogs, changes in hair color and structure can occur before the development of scales and crusts.
Readers also liked: Canine Follicular Dysplasia
Short-haired dogs, such as Vizslas, tend to develop superficial pyoderma with papules, pustules, collarettes, and circular areas of alopecia. Long-haired dogs, like Akitas, can develop severe, deep pyoderma with nodules and draining tracts.
The condition can be painful, and the combination of follicular casts and draining purulent material can create hair mats and significantly impact the quality of life of the affected dog.
Here are some common clinical signs of sebaceous adenitis in different breeds:
It's essential to address diagnostic differentials such as demodicosis, dermatophytosis, and staphylococcal folliculitis by obtaining deep skin scrapings and samples for cytology and fungal culture. The distribution of the lesions can be a useful hint, as staphylococcal folliculitis typically affects the trunk, while sebaceous adenitis characteristically starts on the head.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis can be a bit of a challenge with sebaceous adenitis, as it's often underdiagnosed in dogs. This is because the symptoms can be similar to other conditions, such as bacterial folliculitis and demodicosis, dermatophytosis, endocrinopathy, and more.
A diagnosis requires multiple punch biopsies analyzed by a dermopathologist, who will look for granulomatous or pyogranulomatous inflammation surrounding the sebaceous glands or even complete destruction of sebaceous glands. This is the only way to confirm the presence of sebaceous adenitis.
Other conditions that can present similarly include bacterial folliculitis, demodicosis, dermatophytosis, endocrinopathy, pemphigus foliaceus, zinc responsive dermatosis, vitamin A-responsive dermatosis, ichthyosis, and nutritional deficiencies.
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosis of sebaceous adenitis requires a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests. The gold standard of diagnosis is punch biopsy, which involves taking two 6mm punch biopsies along the back of the neck between the neck and withers, and in any affected areas.
Biopsy samples are then analyzed by a dermopathologist to comment on the condition of the sebaceous glands. This helps to confirm the diagnosis of sebaceous adenitis, which is often underdiagnosed in dogs.
Other conditions with similar presentations, such as bacterial folliculitis and demodicosis, dermatophytosis, and endocrinopathy, must also be ruled out through diagnostic tests. These conditions can present with similar symptoms, making diagnosis challenging.
To confirm a diagnosis of sebaceous adenitis, multiple punch biopsies are typically analyzed by a dermopathologist. This involves examining the condition of the sebaceous glands, which may show granulomatous or pyogranulomatous inflammation.
The diagnostic process can be complex, involving a range of tests and evaluations. However, with the right approach, a diagnosis of sebaceous adenitis can be confirmed, allowing for effective treatment and management of the condition.
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosis is a crucial step in understanding and treating any condition. Acne is a common differential diagnosis for neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis.
Acne can present with similar symptoms, including skin inflammation and lesions. Rosacea is another condition that may be mistaken for neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis due to its similar symptoms.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a condition that can also be confused with neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis. Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, also known as Sweet syndrome, is a rare condition that shares some symptoms with neutrophilic sebaceous adenitis.
Other conditions that may be considered in the differential diagnosis include Jessner lymphocytic infiltrate.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sebaceous adenitis painful for dogs?
Sebaceous adenitis in dogs is typically not painful, but it can lead to secondary infections that cause discomfort and further skin damage.
What shampoo is good for sebaceous adenitis?
For sebaceous adenitis, your vet may recommend a medicated shampoo containing sulfur and/or salicylic acid, such as Virbac Keratolux. This can help manage symptoms and promote healthy skin.
What food is good for dogs with sebaceous adenitis?
Dogs with sebaceous adenitis can benefit from a diet rich in omega-3 and -6 fatty acids, found in foods like Hill's Science Diet Sensitive Skin or Royal Canine Skin Support
What are the symptoms of sebaceous adenitis in humans?
Sebaceous adenitis symptoms include red, itchy skin patches on the face, forehead, and torso, which may appear as a rash or pustules, often triggered by sunlight
Is sebaceous adenitis curable?
Sebaceous adenitis is a lifelong condition, and while treatment options are available, there is no cure. Treatment effectiveness varies, but multiple options can help manage the disease.
Sources
- https://todaysveterinarypractice.com/dermatology/sebaceous-adenitis-in-companion-animals/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sebaceous_adenitis
- https://dermnetnz.org/topics/neutrophilic-sebaceous-adenitis
- https://vetfocus.royalcanin.com/en/scientific/canine-sebaceous-adenitis
- https://www.samoyedhealthfoundation.org/diseases/sebaceous-adenitis-sa/
Featured Images: pexels.com


